Creating a secure environment for businesses is crucial for protecting assets and personnel, all while ensuring seamless daily operations. Access control systems, particularly those utilizing badges or access cards for employees, have become a popular choice in managing facility access. This article delves into the intricacies of badge access systems, covering various aspects from the types of employee badges to the components of office badging systems, authentication methods, and setup. Additionally, it explores the advantages and disadvantages of employing a badge security system.
What is an Employee Badge Access Control System?
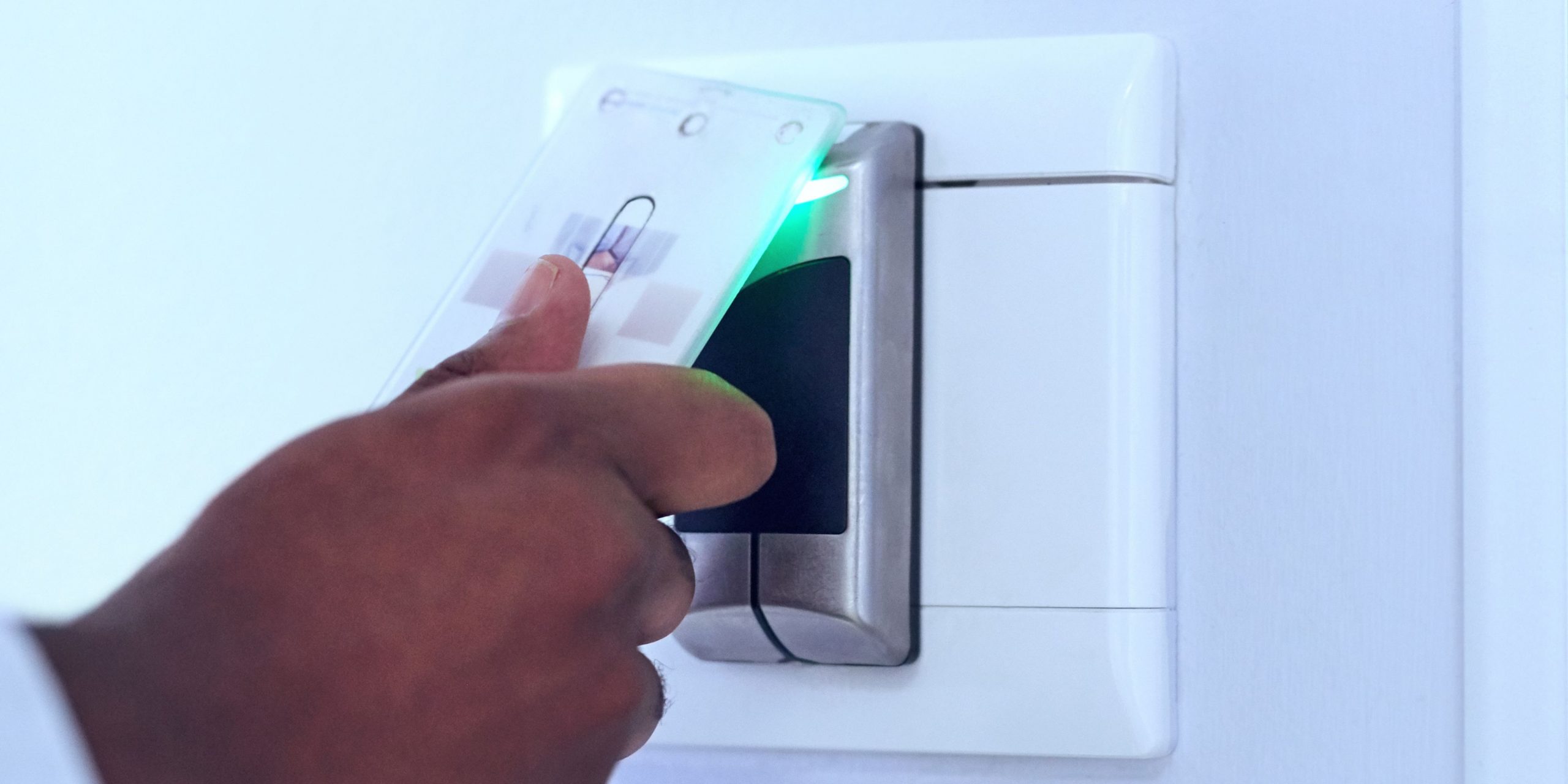
A security badge system is a form of access control that employs ID badge cards to authenticate individuals requiring access to specific locations or resources. These badges typically contain information like a photo, name, or unique identification number, along with a means for users to authenticate themselves on electronic badge readers. Common access badges utilize technologies such as proximity cards, RFID, or magnetic stripes.
How Does an Employee Badge Entry System Work?
An employee badge entry system operates through three simple steps:
- An employee presents their badge to the badge reader, either by holding an RFID badge near the device or swiping it through an electronic reader.
- The badge reader authenticates the data encoded in the badge, verifying it against the business’s identification databases.
- Based on the credentials and permissions of the user, the door is either unlocked or remains locked.
Where are Employee ID Badge Systems Installed?
Badge access control systems find applications in various settings such as offices, schools, hospitals, and other organizations. They are designed to:
- Enhance security by controlling access to sensitive areas.
- Automate the authentication process, streamlining resource access.
- Monitor individuals’ movements within a facility by logging badge system scans.
These systems can be augmented with additional security measures like security guards, cameras, or alarms for heightened security.
Components of an Employee Badge System
A typical badge access door system comprises three main components:
- Badges: These identification cards store user information, including their name, ID number, and security level, and are required for accessing secure locations.
- Card Readers: Devices used to read credential information and grant access based on individual permissions set by an administrator. These readers analyze badge information, verifying the user’s identity swiftly and accurately.
- Magnetic or Electronic Door Locks: These locks secure doors physically, activated or deactivated by the badge reader system, allowing or denying access to users.
Types of Employee Badge Entry Systems
While employee ID badge systems may seem similar, there are various access control reader options available today. Common types include:
- RFID Employee Badging Systems: These badges emit a radio signal read by an antenna, allowing effective contactless badge access.
- Swipe Access Badges: Users manually swipe these cards through electronic readers, granting access. They are easily updatable based on access level changes.
- QR-Code Badge Entry Systems: QR codes are scanned by specialized readers, with information accessed online through secure servers. They are cost-effective but pose a security risk due to easy replication.
- Digital Access Badges: With mobile access gaining popularity, digital versions of ID badges within access apps eliminate the need for physical cards, enhancing convenience.
Applications for Office and Employee Badging Systems
Employee badging systems offer numerous use cases beyond front door access:
- Controlling Access to Resources: Access to computers, networks, and other physical or data resources can be managed using employee ID badge systems.
- Timekeeping: Employees can record their hours for payroll or accounting purposes by scanning their ID cards.
- Attendance Tracking: Access badge logs aid supervisors in optimizing schedules and are essential for mustering during evacuations.
- Security Monitoring: Real-time access badge logs alert managers to potential security issues, enhancing facility security.
Benefits of Badge Security Systems
Implementing badge security systems offers several advantages:
- Improved Security: Access control helps monitor and record entry, preventing unauthorized access. Lost or stolen badges can be deactivated.
- Enhanced Visibility: Employers can monitor attendance and access, identifying suspicious activities promptly.
- Increased Efficiency: Manual record-keeping is reduced, streamlining processes.
- Effective for Multiple Entry Points: Access badges can secure various access points, simplifying access control.
- User Convenience: Employees find badge systems convenient, eliminating the need for manual credentials.
Drawbacks of Badge Door Reader Systems
However, there are some disadvantages to consider:
- Reliability Issues: Damage or improper reading of badges can lead to access failures. Interference from other signals might also cause problems.
- Dependency on Electricity: Badge systems require electricity, making them unsuitable for locations with limited power supply. Backup power sources are recommended.
- Financial Costs: Maintaining physical badges and readers can be costly over time.
- Security Risks: Outdated technology may pose vulnerabilities, allowing hackers to access sensitive information.
Visitor vs. Employee Badge Systems
While both systems share technology, visitor and employee badge systems differ. Visitor badges often have limited permissions and pose security risks due to lack of unique identification information. It is recommended to combine visitor badge systems with check-in protocols and temporary access restrictions to mitigate potential security breaches. Unlike employee badges, visitor badges may not contain comprehensive identification details, making it essential to implement additional security measures. Visitor badge systems should be designed with clear expiration protocols, ensuring that temporary access is restricted after a predetermined period. Regular audits and updates to visitor databases are crucial to maintaining an effective visitor badge system.
In contrast, employee badge systems are more intricate, integrating various authentication methods and access control features tailored to individual roles and responsibilities within the organization. Employees typically carry badges containing detailed identification information, allowing for precise access control and seamless integration with other security measures. These badges are an integral part of the organization’s security infrastructure, enabling employees to navigate the workplace efficiently while maintaining strict access controls.
Ultimately, businesses should strike a balance between convenience and security when implementing both visitor and employee badge systems. By understanding the unique requirements of each system and addressing potential vulnerabilities, organizations can create a comprehensive access control strategy that safeguards their premises and personnel effectively.